Technology and its products are often causative: a technology might be applied to develop more effective and intelligent products, which in turn can play an important role in advancing that technology.
This interrelationship may be observed in metalworking. Over the last few years, leading-edge technology has resulted in multitasking machine tools and machining centers with impressive working possibilities. At the same time, this progress in machine tool engineering is significantly changing metal cutting technology.
The advanced multifunctional machine tools increasingly widen the range of machining operations that can be performed. Technological processes developed for these machines are oriented to maximize machining operation for one-setup manufacturing, creating a new source for more accurate and productive manufacturing. Milling gears and splines is one of the operations suitable for performing on the new machines.
Traditionally, gear (and spline) making is a complicated process that involves milling, chamfering, grinding and other operations. With batch manufacturing, the majority is made on specific machines: gear hobbing, gear shaving, gear grinding and so on. Developments in technology have changed the limits of hardness for cutting and considerably increased operational accuracy. This in turn has reduced abrasive machining in gear making while decreasing rough cutting. The modern multifunctional machines, which meet the requirements of one-setup manufacturing, have proved to be perfect for various gear making operations.
These new machines require appropriate tooling and cutting tools manufacturers should prepare their response accordingly, which is why producers of general-purpose rotating cutting tools are reconsidering the role of gearmilling cutters in their program for standard product lines.
ISCAR, a leader in the cutting tool industry, is embodying this trend with a three-point program for form gear-making tools:
- Milling cutters carrying indexable inserts
- Milling cutters with replaceable cutting heads based on the T-SLOT concept
- Milling cutters with replaceable MULTIMASTER cutting heads
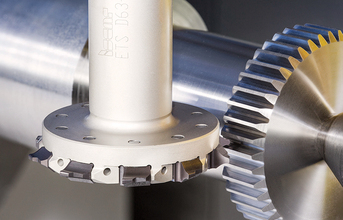
MODUGEAR, the family of indexable gear-milling cutters reflects a conventional design approach, comprising disk-type tools with tangentially clamped LNET inserts. The tangential clamping principle provides an extremely rigid and durable cutter structure that results in stable and precise enough machining tooth or spline profiles. Its principal application is producing involute gears of relatively low accuracy and rough gear-milling operations that feature a 1-1.75 mm gear module range.
The cutters with replaceable heads have two significant advantages compared with gear milling tools carrying indexable inserts: they offer better precision and allow the design of gear-milling cutters that are small in diameter but feature quite a large number of teeth. The replaceable heads are mounted in bodies (shanks), which are standard-line products suitable not only for the gearmilling heads but also for other types of head (for milling slots and grooves, for example). This enables customers to increase operating efficiency of the versatile shanks and to reduce tool stock, providing added value.
The replaceable solid carbide heads of the T-GEAR SD D32-M-SP15 family are mounted in standard T-SLOT SD-SP15 cylindrical shanks and transform the latter into 32 mm diameter gear milling cutters The precise profile of the cutters' teeth and the accurate and reliable SP-connection between the shank and the head define its range of use: milling involute gears featuring a 1-2 mm module.
Both types of milling cutters (those with indexable inserts and those with replaceable heads) meet the requirements of standard DIN 3972, basic profile II.
There are two types of MULTI-MASTER spline and gear making solid carbide heads. The first type is represented by the MM SS heads that were specially designed for milling involute spline shafts, specified by DIN 5480 and ANSI B92.1 standards. These heads are intended for 1, 1.25, 1.5, 3 mm module (DIN 5480) and 8, 10, 12, 24 diametral pitch (ANSI B92.1).
The heads of the second type, MM SG, are used in milling spur gears in accordance with DIN 3972 (module 1-1.75 mm) and ANSI B6.1 (diametral pitch 15-24) standards.
The main application field for MULTI-MASTER heads is the efficient production of small to medium batches of spline and spur gears in various industrial branches.
The world of gears is very rich and multiform, embracing a wide variety of external and internal gears: spur, helical, bevel, hypoid, and more. Manufacturing these gears encompasses an entire, dynamic industrial sector with its own methods, equipment and tooling. The introduction of multitasking machines in gear milling as a serious alternative to a dedicated machine represents a new challenge to this sector and producers of commonly-used cutting tools should be ready for this significant change. ISCAR meets this challenge while maintaining the requisite high standards demanded by end users.
Source: ISCAR



























