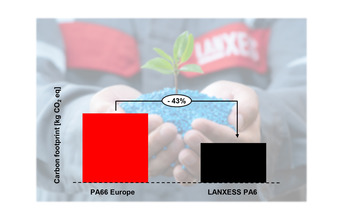
The Durethan-brand polyamide 6 compounds from LANXESS are not only cost-effective alternatives to polyamide-66-based compounds but are also much more climate-friendly. This is according to calculations performed by the speciality chemicals company based on its own data and on figures published by a range of institutions including various associations of the plastics industry.
"With 3.66 metric tons of CO2 equivalents emitted per metric ton of material produced, the carbon footprint of our polyamide 6 base resin is much more than 40 per cent lower than the current published European industry average for polyamide 66," says Dr Guenter Margraf, Head of Sustainability and Product Management in High-Performance Materials. "The carbon footprint of our polyamide 6 compounds is therefore also correspondingly smaller, which is why they are the perfect substitute for polyamide 66."
Glass fibers made from waste glass
The carbon footprint of the polyamide 6 compounds from LANXESS can be reduced even further by producing them not from conventional glass fibers, but from the resource-conserving Eco glass fibers developed by the company. Industrial glass waste is used in their production, which reduces the consumption of raw materials and energy and avoids waste.
"The carbon footprint of our Eco glass fibers is around two-thirds smaller than that of conventional glass fibers," says Margraf. LANXESS offers the corresponding compounds that are mass-balanced in accordance with ISCC Plus ("International Sustainability and Carbon Certification") under the brand name Durethan ECO. They contain up to 60 per cent by weight of recycled fiber. Mass balancing helps to determine the share of sustainable material in the compound and to indicate it in a transparent manner for processors.



























