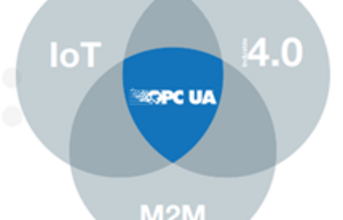
OPC UA Interoperability for Industry 4.0 (Source: opcfoundation.org)
Think about a production plant or a manufacturing unit; it is a visual cacophony of machines, robots, assembly lines, drives and many more parts, yet completely (almost!) synchronised and working together. Bringing all of them together is the Industrial Internet of Things coupled with the open, Ethernet-based OPC UA communication standard that forms a critical part of the industrial automation landscape.
OPC UA integrates IT/OT technologies with diverse products, solutions, and services across factory and process systems. Whether it is the security measures, networking, establishing standardised communication or needing vendor and platform neutrality, OPC UA lays the foundation for digitised industrial automation.
It is a fact that automation in the industrial world opens doors for new business opportunities, enhanced solutions, and services. But the reality faced is how to effectively transfer the raw data generated from the shop floor equipment to the business applications like ERPs and CRMs, and draw insights to make actionable decisions for a competitive advantage. Hence, there is an imminent need to fully automate the manufacturing process and access real-time and accurate information from these systems for analysis, machine alerts, maintenance notifications etc.
OPC UA is the open-source communication standard platform explicitly designed for achieving industrial interoperability. It acts as a bridge that connects the IT (Information Technology) with the OT (Operational Technology) and for information exchange between the various assets in the OT layer.
Industry 4.0 mandates interoperability and standardised data connectivity for meeting its specific requirements, including but not limited to,
- Integration across all levels
- Secure transfer and authentication at user and application levels
- Conformity to industry standards
- Scalability
OPC UA serves as the common data connectivity and collaboration standard that enable interoperability of local and remote device access in IoT, M2M, and Industry 4.0 settings.
Limitation & Challenges of Industrial Interoperability
It is essential to establish seamless interoperability between the enterprise's components and the automation systems. Over the years, industries have faced many challenges in building a unified structure that connects all the components, from factory floor devices to host applications. OPC UA serves as the common data connectivity and collaboration standard that enables local and remote device access interoperability in IoT, M2M, and Industry 4.0 settings. We are now closer to the goal of building a unified system that delivers reliable interoperability, thanks to the development of OPC Unified Architecture and its easy implementation in the embedded layer.
However, it is important to understand the challenges associated with implementing industrial interoperability.
- Standardisation
IIoT researchers state global standardisation as one of the top challenges for industrial interoperability. Industries use systems from various manufacturers and follow unique processes. So, it can be difficult to come up with a one-size-fits-all solution.
- Compatibility and connectivity issues
There is a gap in the communication between the existing resources and the production process. In most cases, industries have islands of data maintained and accessed by different teams. Creating a cohesive network that can build a bridge between these data islands can be a huge challenge for developers.
- Security
Data security is one of the critical factors that need to be considered while implementing industrial interoperability. With all the data accessible from one-point, cyber threats and hacks also rise. Therefore, security needs to be strongly considered while building an interoperable system.
- Usage access
It is important to clearly define who will be given access and what they can access. Monitoring accessibility, especially on the production floor, can be a huge challenge for all stakeholders.
- Cost
The cost can be a huge limiting factor when you completely overhaul the existing system in the initial stages. Many companies worry about the returns on investment and hesitate to invest in OPC UA solutions. Therefore, it is important to work with experts with domain expertise and in-depth experience in OPC UA to maximise your time spent and investment made.
OPC-UA - A Key Enabler For IIoT
There is a simple analogy for OPC-UA. Currently, OT systems & IT systems speak different languages in various heterogeneous protocols. For example, machines speak Japanese or German, and our IT systems speak English. And as a result, they can't talk to each other besides basic hand signals. Enter OPC-UA! A translator that allows them to talk to each other in the same language and thus homogenise the data exchange for better horizontal and vertical integration of assets in OT and IT.
There is much more scope for implementing analytics at the top level when inter-machine communication or direct communication between assets and enterprise applications. This ability to enable interoperability in manufacturing facilities has led to OPC-UA being called an "IIoT Enabler and Conqueror of the Cloud" by the International Society for Automation (ISA) and "The Global Production Language" by VDMA, respectively.
It is important to understand the OPC-UA is not a communication protocol but a communication platform. It provides a mechanism to model everything from factory data to parts of the entire factory itself. OPC-UA works in conjunction with a host of other communication protocols such as MQTT, AMQP, Profinet, Ethernet/IP, etc.
OPC UA enables semantic mapping of various information models to represent the actual products and their product steps and thus ensures that these products can plug and produce. The below image shows how OPC-UA has a role to play across the different layers in an Industrial Automation setup for various products.

Image.2. OPC UA Interoperability across the Automation Pyramid
OPC-UA & Cybersecurity of Modern Industries
OPC-UA enables both horizontal and vertical integration, as well as the communication and management of devices and data from every part of the network, from the field to the enterprise. Manufacturing organisations and our customers are looking for continuous strategies to improve their cybersecurity strategies and implementation. A core pillar of OPC UA is the focus on security, not just for data integrity reasons but also service availability.
The OPC UA Specs summarise the security focus in three areas:
- Authentication between client and server applications
- The ability to determine whether a user is authorised to connect and/or perform the requested action
- The confidentiality and integrity of the communications.
OPC-UA provides communication layer security by ensuring,
- Data Confidentiality: Encrypting of messages
- Data Integrity: Signing of messages
- Data Availability: Minimal message processing before authentication
OPC-UA provides application-layer security by ensuring,
- Authentication of applications: Ensuring exchange of application instance certificates
- Authentication of users: Username, password, security token, certificates
- Auditability: Generating audit events for security operations
It is important for manufacturing organisations to understand that there are other security-related factors to be considered outside of OPC-UA in their cybersecurity implementations, such as,
- Data Ownership: Where the data resides and who has access to this
- User Management: Ensuring password policy rules are in place
- Organisation Issues: Physical access control and security policies in secure zones
Having OPC-UA natively implemented in systems provides a starting point to ensure secure data communication. But the key cybersecurity issues associated with the opening of ports, security levels and related matters fall in the hands of IT teams in manufacturing organisations from a business context.
With the evolution of open standards in Industry 4.0 and IIoT process control, most DCS/PLC vendors have adopted OPC UA as an interoperable standard for distributing data streams to consuming edge applications like SCADA, PI, Historian, Alarm Logger, ERP etc. And this has resulted in exponential growth in deployments. And with leading cloud providers like Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and IBM Watson already acknowledging the benefits of OPC-UA for moving shop floor data to the Cloud, this adoption will only increase in the next few years. This is primarily because OPC-UA has been developed to be secure by design and includes semantic information models that ensure that data is easily consumed by enterprise and cloud applications to realise IIoT and digital transformation solutions for manufacturing organisations.


























